The "SMTP Receiving" tab allows you to configure parameters relative to this specific service's configuration, to add listeners, and manage access to the service by adding rules applicable to all existing listeners.
Listeners and control rules
Listeners
The first section in the SMTP Receiving tab is "Listeners". In this section, you can add, delete, or edit the TCP socket listeners for the SMTP Receiving service.

Editing one of the existing listeners will result in accessing two configuration pages: "General" and "SSL Settings". The same pages will also be displayed when hitting the "Add Listener" button and choosing the "Advanced Config" option.
By default the listeners will be configured on 0.0.0.0 (IP block containing all possible configured IPv4 addresses) and :::(IP block containing all possible configured IPv6 addresses) port 25, the standard port (non-SSL) for SMTP communication and 465 port used for implicit TLS.
Access control
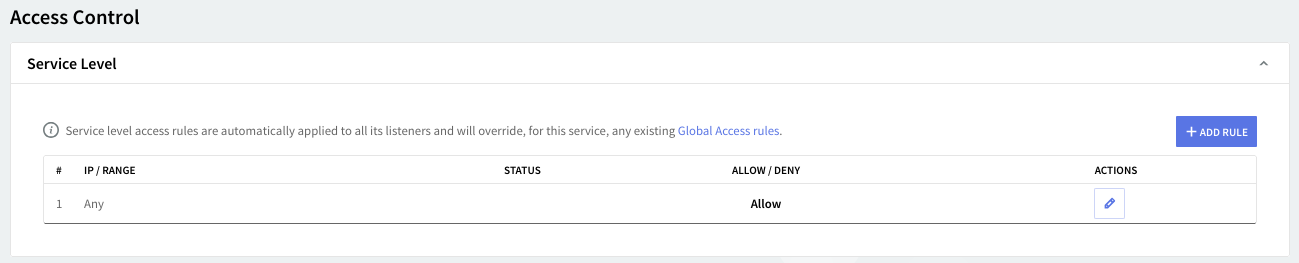
Access rules allow you to control connection to this service from specific Networks / IP Ranges / IPs.
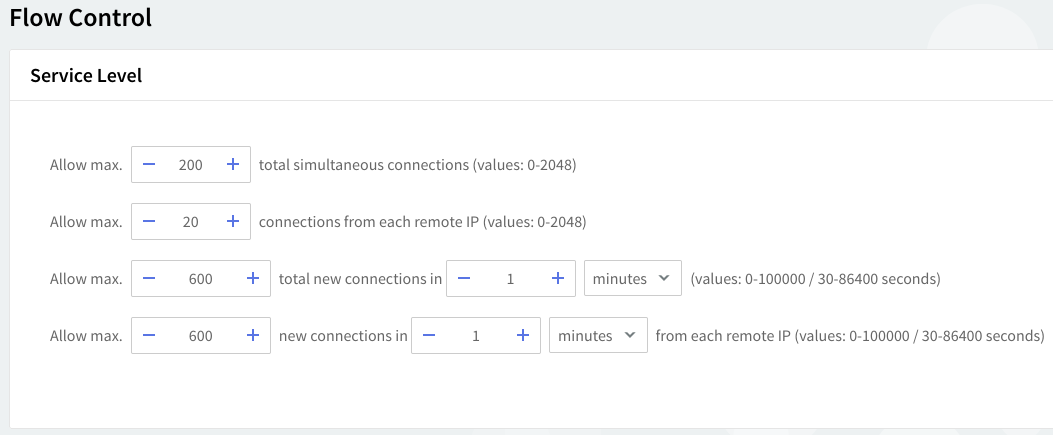
Flow control
Service configuration
The service flow control context allows you to define the max connections, max connections/interval, max peer connections, and max peer connections/interval values.
Logging
You can select several types of messages to be logged for the SMTP Receiving service: critical messages, error messages, warning messages, informational messages, and protocol communication. To choose which messages to log, click the "Log Level" slider and move it to the left or right. The selected types of messages will change color from whiter to blue.
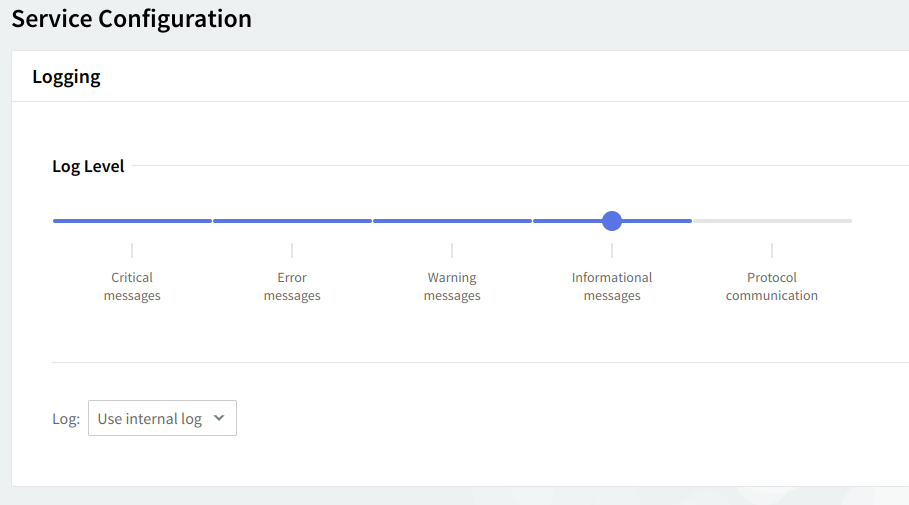
Log files can be stored using your internal log files, your system's log files or within the log files located on a remote system. Use the "Log" drop-down menu to select where to save your log files.
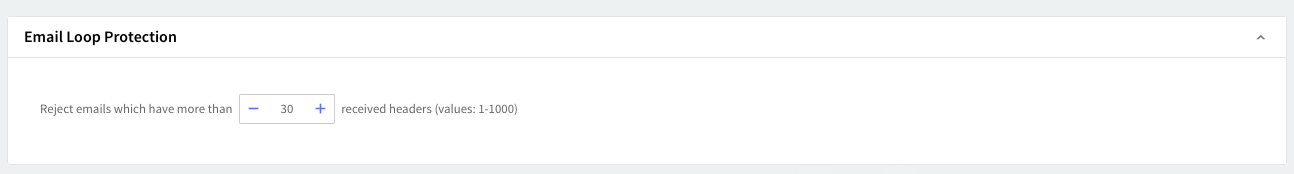
Email loop protection
A looping message is an email sent from one mail server to another, without reaching its destination. Whenever an email is processed by a mail server, a "Received" header is appended to it. To prevent excessive traffic on your mail server, enable the "Email Loop Protection" option and specify a maximum number of "Received" headers for incoming emails. This feature helps avoid an infinite email loop caused by misconfigurations. You can set values between 1 and 1000, though the default value of 30 is recommended.
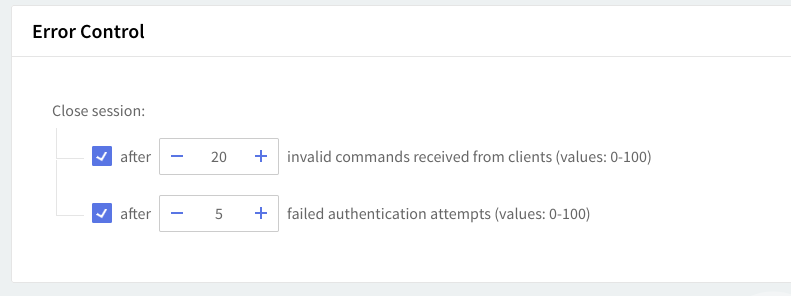
Error control
To set a maximum allowed number of errors caused by invalid commands received from clients or by failed authentication attempts, check the related options in the Error Control area. Use the up and down arrows corresponding to each of these options to set a specific number of errors.
A value of 0 means that the respective limit is disabled (no limit is imposed).
Thread management
Thread management allows you to set different numbers of processing threads for the SMTP Receiving service, depending on your traffic load. First, using the up and down arrows, set a number of threads to be allotted when the SMTP Receiving service is started. To have a different number of threads for peak periods, check the overload option and use the up and down arrows to choose the thread number.
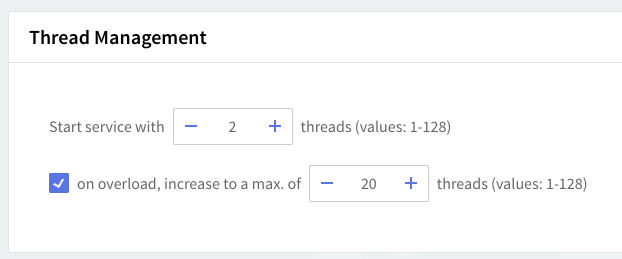
Depending on your SMTP Receiving service load you can increase the number of processing threads which can lead to increased performance and response time for this service. However, this increase should be made very carefully, and making sure that the server hardware can provide the processing and memory resources required by a higher number of threads. The default setting of 2 starting threads and an increase on overload to 20 threads is recommended.
When you are done configuring these parameters, remember to hit the "Save Configuration" button to preserve your changes.